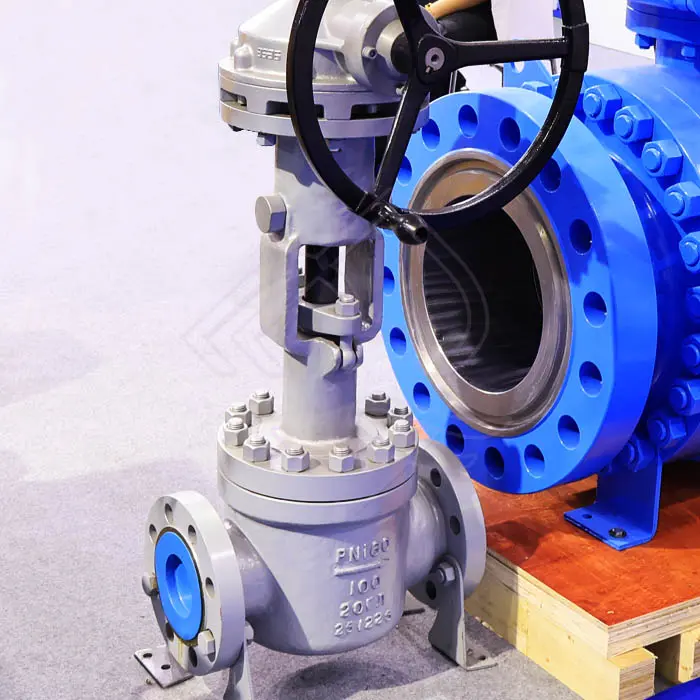
Orbit Ball Valve Manufacturer
Working Principle
The orbit ball valve operates on a two-step motion principle: lift and rotate. When the handwheel or lever is actuated, the stem mechanism first lifts the ball away from the valve seat. Once disengaged, the ball rotates freely by 90 degrees to the open or closed position. During closing, the reverse motion occurs—the ball rotates back into position and then is mechanically forced into the seat to achieve tight sealing.
Because the ball does not rub against the seat during rotation, the orbit design eliminates galling and minimizes abrasion, ensuring longer seat life and consistent sealing performance over repeated cycles. This feature distinguishes orbit ball valves from standard floating or trunnion-mounted ball valves.
Manual Operation
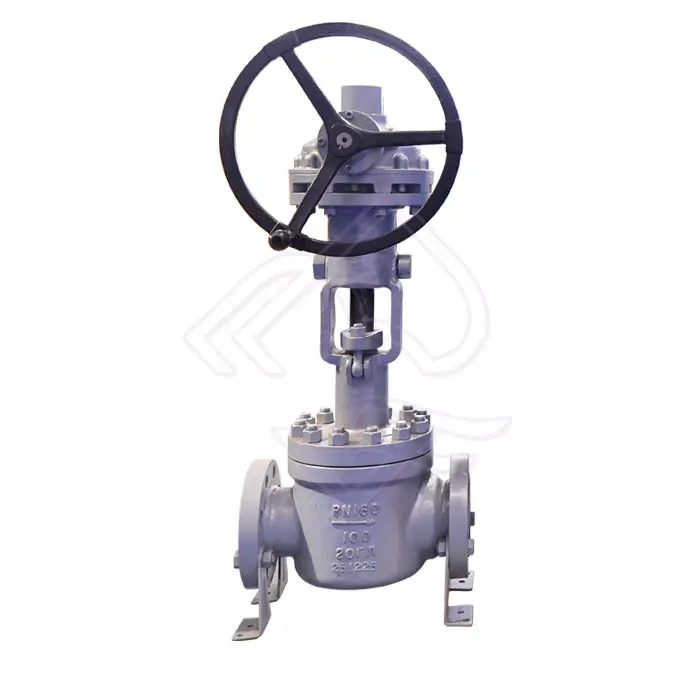
The valve is manually operated, typically using a handwheel, gear operator, or lever depending on valve size and pressure rating. Manual actuation provides precise control, reliability, and independence from external power sources, making it especially suitable for remote locations or safety-critical systems.
For larger diameter valves or higher pressure classes, a worm gear or bevel gear operator is commonly used to reduce operating torque and allow smooth, controlled operation. Manual operation also simplifies maintenance and reduces overall system complexity.

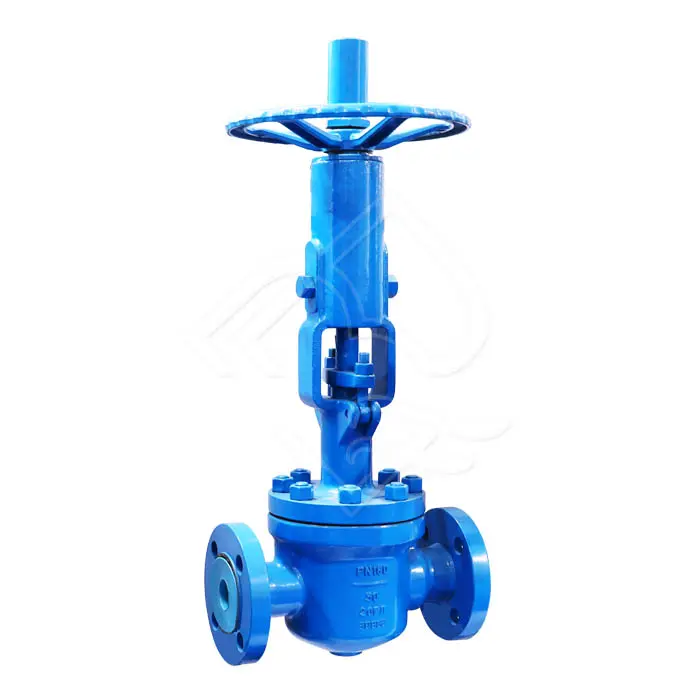
Flange End Connection
The flange end design allows direct bolting to pipeline flanges, providing a robust, leak-tight connection. Flanged ends are widely used in industrial piping systems due to their ease of installation, alignment accuracy, and convenience during maintenance or replacement.
Manual operated flange end orbit ball valves are typically manufactured in accordance with international standards such as ASME B16.5, ASME B16.47, EN 1092, or DIN flanges, and are available in a wide range of pressure classes, including Class 150, 300, 600, 900, and higher upon request.
Construction and Materials
Orbit ball valves are engineered for durability and performance. Common construction materials include:
Body and Bonnet: Carbon steel (ASTM A216 WCB), stainless steel (CF8, CF8M), alloy steel, duplex stainless steel, or other special alloys
Ball: Stainless steel or alloy steel with hard-facing or surface coatings for wear resistance
Seats: Metal-seated or soft-seated designs using PTFE, reinforced PTFE, graphite, or hard metal materials
Stem: High-strength stainless steel with anti-blowout design
Gaskets and Seals: Graphite, PTFE, or metal seals for high-temperature service
The valve design often incorporates fire-safe construction, anti-static features, and pressure-relief mechanisms to meet stringent safety requirements.
Sealing Performance
One of the key advantages of the orbit ball valve is its excellent sealing capability. The mechanical seating action ensures consistent contact pressure between the ball and seat, resulting in bubble-tight shutoff even under fluctuating pressure and temperature conditions.
Metal-seated orbit ball valves are particularly suitable for applications involving high temperatures, abrasive media, or frequent cycling. The controlled seating force reduces seat deformation and ensures reliable performance over the valve’s service life.
Advantages
- Manual operated flange end orbit ball valves offer numerous operational and economic benefits:
- No sliding contact between ball and seat during rotation
- Extremely low wear and extended service life
- Reduced operating torque compared to traditional ball valves
- Reliable tight shut-off under high pressure and temperature
- Suitable for frequent operation and severe service conditions
- Simple manual actuation with high operational reliability
- Easy installation and maintenance due to flanged connections
These advantages make orbit ball valves a preferred choice in applications where standard ball valves may fail prematurely.
Applications
- Manual operated flange end orbit ball valves are widely used across multiple industries, including:
- Oil and gas production and refining
- Petrochemical and chemical processing plants
- Power generation systems
- Natural gas transmission and distribution
- Steam and thermal oil systems
- Water treatment and industrial utilities
They are especially effective in services requiring tight shut-off, high cycle life, and resistance to wear, such as isolation of high-pressure process lines or handling of corrosive and high-temperature fluids.
Standards and Testing
Orbit ball valves are designed and manufactured in compliance with international standards such as API 6D, API 608, ASME B16.34, and ISO 17292. Each valve typically undergoes rigorous testing, including hydrostatic shell testing, seat leakage testing, and operational torque verification to ensure performance and safety.
Fire-safe testing in accordance with API 607 or API 6FA may also be provided upon request, depending on application requirements.